Random generation of a data base


Next: Formulation of the
Up: LOAD POWER MARGIN
Previous: Contingency severity for
Computer based learning techniques need a representative sample of
power system situations, for which topology 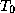 , electrical state
, electrical state
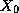 and margins
and margins 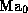 and
and 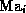 are pre-determined.
The construction of such samples calls for random sampling techniques
similar to those developed in the decision tree approach to power
system security assessment [8], and exploits an
appropriate ``system-theory'' LPM computation method.
are pre-determined.
The construction of such samples calls for random sampling techniques
similar to those developed in the decision tree approach to power
system security assessment [8], and exploits an
appropriate ``system-theory'' LPM computation method.

Figure 3: Principle of the data base generation
The overall principle of such a data base generation is depicted in
Fig.
3, where we consider a total number of
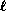 different contingencies,
different contingencies,  different candidate attributes, and
an overall sample of
different candidate attributes, and
an overall sample of 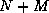 operating states, where
operating states, where 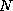 denotes the
number of states used in the learning set to derive the approximate
models, and
denotes the
number of states used in the learning set to derive the approximate
models, and 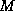 the number of independent test states used
subsequently to validate them.
the number of independent test states used
subsequently to validate them.
The random sampling approach aims at screening all relevant power
system situations, and in particular normal (usual) states as well as
weak situations. The power system engineers are generally able to
provide valuable prior information helping to determine the considered
random variations (e.g. load level, generation schedule, topology, voltage set points ...).
Wed Jan 18 20:00:51 MET 1995
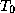 , electrical state
, electrical state
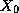 and margins
and margins 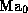 and
and 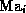 are pre-determined.
The construction of such samples calls for random sampling techniques
similar to those developed in the decision tree approach to power
system security assessment [8], and exploits an
appropriate ``system-theory'' LPM computation method.
are pre-determined.
The construction of such samples calls for random sampling techniques
similar to those developed in the decision tree approach to power
system security assessment [8], and exploits an
appropriate ``system-theory'' LPM computation method.

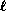 different contingencies,
different contingencies,  different candidate attributes, and
an overall sample of
different candidate attributes, and
an overall sample of 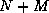 operating states, where
operating states, where 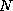 denotes the
number of states used in the learning set to derive the approximate
models, and
denotes the
number of states used in the learning set to derive the approximate
models, and 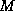 the number of independent test states used
subsequently to validate them.
the number of independent test states used
subsequently to validate them.