Hybrid approaches


Next: Comparative assessments
Up: Classes of methods
Previous: Statistical pattern recognition
Various hybrid approaches combining the above methods have been
proposed in the literature. In the context of our research we have
used the following two.
DT-ANN, consists, in its pure version, of first building a tree
which identifies relevant attributes among candidate ones, then of
translating it into a four layer MLP, further adapted via
back-propagation to improve classification performances. It may or
may not exploit the continuous information provided by security
indices in the latter step. This allows one in practice to improve
the reliability of decision trees while maintaining their advantages
of simplicity and computational efficiency [23]. A
variant of this method consists of using a fully connected three layer
perceptron, with an a priori fixed number of hidden units.
DT-NN, consists of using in the distance computation of the
 method only the attributes selected by a decision tree built
for the same problem. In our simulations, the attribute values are
pre-whitened
method only the attributes selected by a decision tree built
for the same problem. In our simulations, the attribute values are
pre-whitened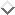 and the Euclidean distance is used, while the
appropriate number
and the Euclidean distance is used, while the
appropriate number 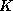 of neighbors is determined by trial and error.
With respect to a non-hybrid nearest neighbor approach, this method is
significantly faster and often more reliable
[24].
of neighbors is determined by trial and error.
With respect to a non-hybrid nearest neighbor approach, this method is
significantly faster and often more reliable
[24].
Wed Jan 18 20:24:41 MET 1995
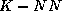 method only the attributes selected by a decision tree built
for the same problem. In our simulations, the attribute values are
pre-whitened
method only the attributes selected by a decision tree built
for the same problem. In our simulations, the attribute values are
pre-whitened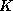 of neighbors is determined by trial and error.
With respect to a non-hybrid nearest neighbor approach, this method is
significantly faster and often more reliable
[24].
of neighbors is determined by trial and error.
With respect to a non-hybrid nearest neighbor approach, this method is
significantly faster and often more reliable
[24].